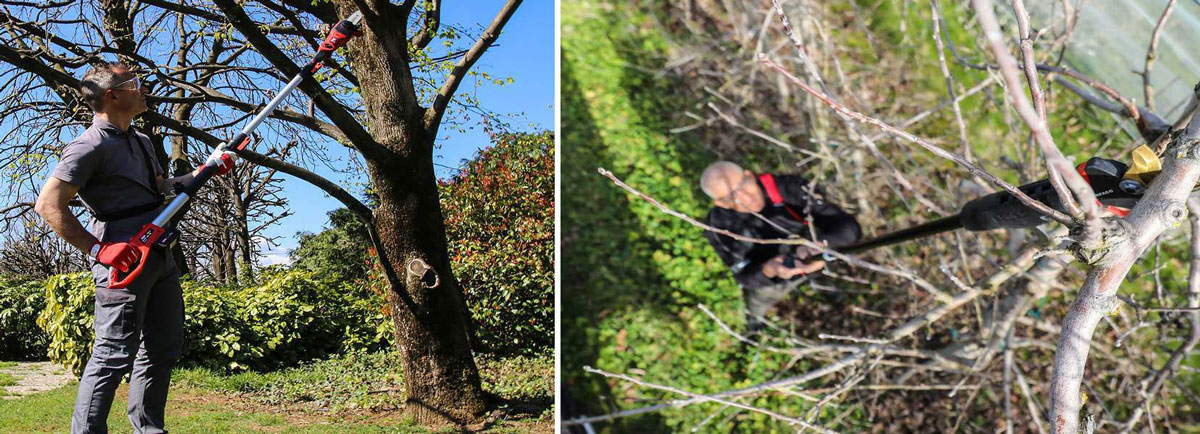
How to choose between a telescopic pruner and a pruning shear? What is the difference between them? Here is a useful article on what sets these two pruning tools apart.
Pruners and pruning shears: which one to chose? A useful article on what distinguishes pruners from pruning shears, Written by real Green and Gardening Experts.
Pruners and pruning shears are employed in the pruning and cutting branches in order to improve the growth, health and fruiting of the plant.
Since their scope of use is the same, when to use a pruner and when to use pruning shears? Which to choose between the two?
First, let’s consider the fact that professionals often use both during their operations, in order to carry out the best possible pruning of each type of branch. However, for the less experienced and hobbyists, we try to summarise in this guide the main aspects that characterise them and their differences, answering all these questions.
CONTENTS
1. Introduction
Let’s now introduce the several subcategories of pruners and pruning shears.
Pruners were developed to meet the need to prune medium and large branches more efficiently and quickly than with manual tools; they are subdivided into:
Pruning shears are divided between battery-powered electric and pneumatic ones.
The battery-powered electric pruning shears represent a state-of-the-art and sturdy alternative to classic manual shears, allowing branches to be cut more rapidly and precisely.
Pneumatic shears are intended for intensive and professional use; in order to be activated, they need to be connected to an air compressor or a motor compressor through a connection hose.
We will summarise the main characteristics and differences between the categories in a table and then analyse them in detail.
| Pruners | Pruning shears | |
| Operation | Petrol / Electric / Battery / Pneumatic | Battery-powered electric / Pneumatic |
| Maintenance | Medium / High Level | Medium / Low Level |
| Cutting capacity | 7 – 30 cm diameter; | 1 – 5 cm diameter; |
| Configurations | Manual / On extension pole | Manual / On extension pole |
| Weight | 1.5 – 12 Kg | 0.7 – 4 Kg |
2. Power supply and Power
The first distinction we can make among these categories is based on their power supply so, basically, their power. The main difference between pruners and pruning shears in terms of power supply is the presence of petrol pruners on the market, which offer a number of advantages and disadvantages compared to other power sources.

Petrol pruners represent the most powerful version of pruning shears and pruners, allowing larger diameter branches to be cut; however, they are the heaviest and most difficult to use, especially in configurations with an extension pole, and require more maintenance.
They are the most polluting and noisiest models.
The petrol engines can be divided into 2-strokes or 4-strokes, with different cubic capacity and power. If you are interested in all the aspects and differences between these two types of petrol engines, read our guide about them.
Here is a table summarising the advantages and disadvantages of petrol-powered models.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Higher power | Heavier |
| Higher cutting capacity | Higher maintenance |
| Noisy | |
| Polluting emissions |
On the other hand, pruners and pruning shears with other power sources are much lighter and more manoeuvrable than petrol models; they require less maintenance and are more environmentally friendly, as they do not produce polluting emissions. However, they offer more limited cutting performance and less power.
Let us summarise in a table the advantages and disadvantages of models with other fuels compared to petrol models.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Lower emissions | Less power |
| Lighter | Lower cutting capacity |
| More silent | |
| Less maintenance |
3. Maintenance
Another aspect that distinguishes pruners and pruning shears is the level of maintenance required. Let us now look specifically at the level of maintenance of the different categories.
One of the most important operations is the maintenance of the cutting device, both for shears and pruners.
For pruning shears, the cutting blades should be cleaned regularly and immediately after use, as sap and various processing residues can damage them if left too long.
For pruners, on the other hand, it is important to correctly adjust the pull of the cutting chain in order to achieve effective pruning results, but also to avoid damaging the cutter bar while working.


In addition to the routine maintenance of the various cutting equipment, different maintenance is also required according to the type of power supply.
3.1 Petrol models maintenance
As said in the previous chapter, we can designate petrol-engine powered pruners as the most maintenance-intensive category due to the greater presence of components subject to wear and tear.
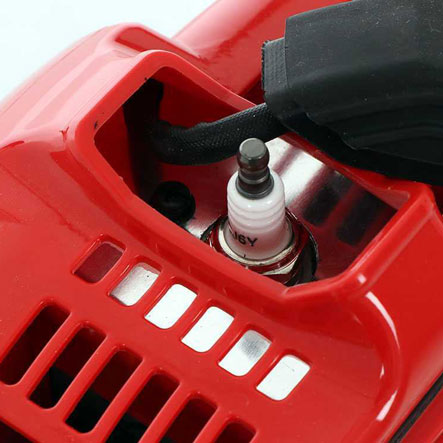
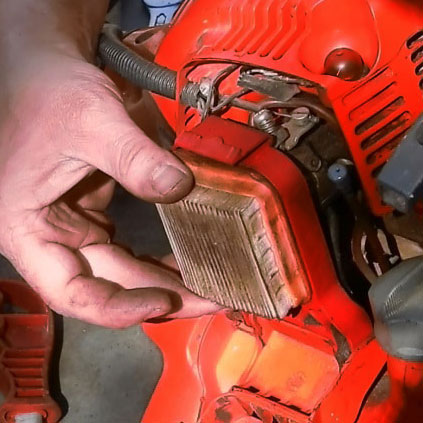
Some examples of the main maintenance procedures for petrol engines are:
- Spark plug maintenance and replacement;
- Air filter maintenance;
- Oil level check



3.2 Pneumatic models maintenance
Immediately after the petrol models, we can mention the pneumatic models of shears and pruners as those requiring the most maintenance.
We can place these categories at a medium level of maintenance, mainly related to the care of the compressor or motor-compressor to which they are to be connected, of their connecting hose, as well as of the cutting apparatus.


3.3 Battery-powered electric models maintenance
Finally, the categories with the lowest level of maintenance required are electric pruners and battery-powered electric pruning shears, where the main care to be taken is related to the care of the batteries and power cables.


To sum up, we will highlight the required maintenance levels of the various product categories in a table.
| 2/4 stroke pruners | Electric Pruners (230V) | Battery-powered pruners | Pneumatic pruners | Battery-powered shears | Pneumatic shears | |
| Maintenance level |    |  |  |   |  |   |
4. Cutting capacity
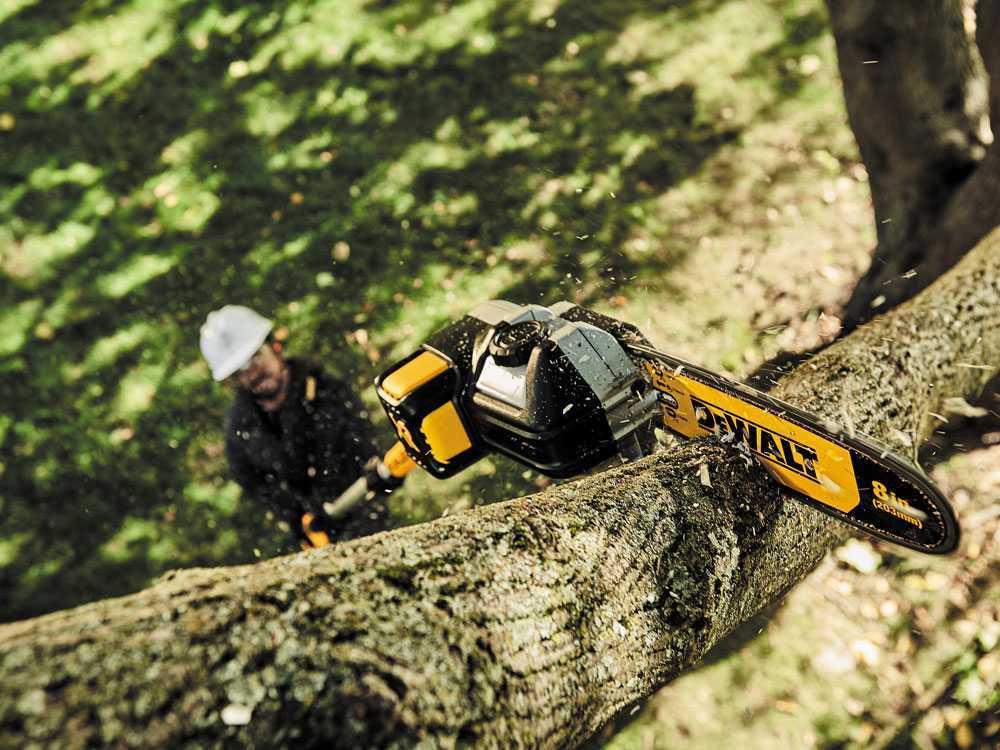

Due to the larger size of the cutting apparatus, pruners are more suitable for cutting medium and large branches.
The aspect that most affects their cutting capacity, apart from their power supply as explained above, is the blade length, which can range from a minimum of 6.5 cm to as much as 30 cm.
The greater blade length and the cutting apparatus size make it possible to cut branches of medium-large diameter, ranging from cutting branches with a diameter of 7-8 cm by using the shorter blades, up to branches of 30 cm diameter by using the longer blades.
Instead, the cut of branches with a diameter of less than 2 cm turns to be ineffective with these tools, since such thin branches are not very stable and, as a result, difficult to cut. For this type of cutting pruning shears are preferred.
| Cutting diameter Petrol pruners | Cutting diameter Electric pruners(230V) | Cutting diameter Battery-powered pruners | Cutting diameter Pneumatic pruners | |
| Hobby use | 80-200 mm | 80-200 mm | 80-200 mm | |
| Semi-professional Level | 150-200 mm | 150-200 mm | ||
| Professional use | 200-300 mm | 200-300 mm | 200-300 mm |
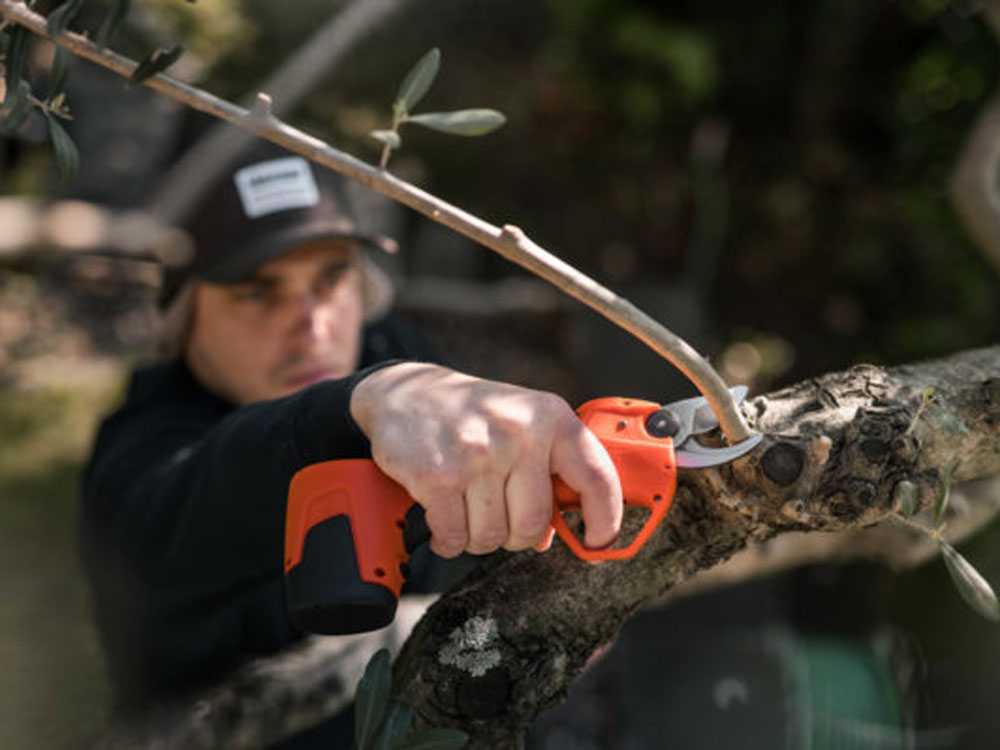

Due to their more compact size and smaller cutting apparatus, shears are usually employed for cutting branches and twigs with a smaller diameter than ones cut with pruners.
The most powerful models can cut branches up to 5 cm in diameter.
They perform a clean and extremely precise cut of the branch, minimising operator effort during operation. In fact, the pressure of the trigger avoids wrist pain and numbness due to the prolonged pressure required by classic shears.
| Cutting diameter Electric Shears | Cutting diameter Pneumatic Shears | |
| Hobby use | 10 – 25 mm | |
| Semi-professional Level | 25 – 40 mm | 25 – 35 mm |
| Professional use | 40 – 50 mm | 35 – 50 mm |
5. Configurations
Both categories can be used in manual version and on an extension pole, in order to comfortably reach even the highest branches. However, they differ in their ease of use. In fact, pruners feature a greater weight and bulk than shears, thus making cutting operations more demanding. Let’s have a close look on what changes for the two configurations.
5.1 Manual configuration
For manual configurations, the main difference between the two tools is their size and therefore the space they require to cut. Pruners feature a larger and bulkier structure and cutting system than shears, and require more space to make the cut, making them suitable for trees with underdeveloped branching.
Instead, the shears, being smaller and lighter, allow less demanding cutting sessions for the operator, and to perform the cut on plants featuring highly developed branching and thick branches close together.
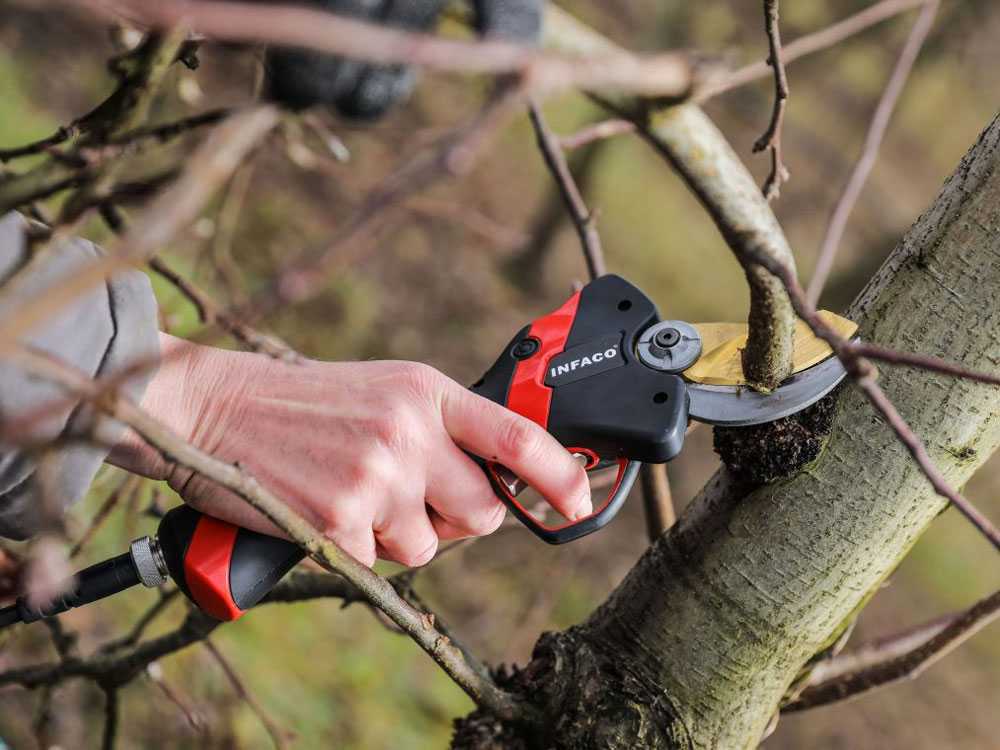
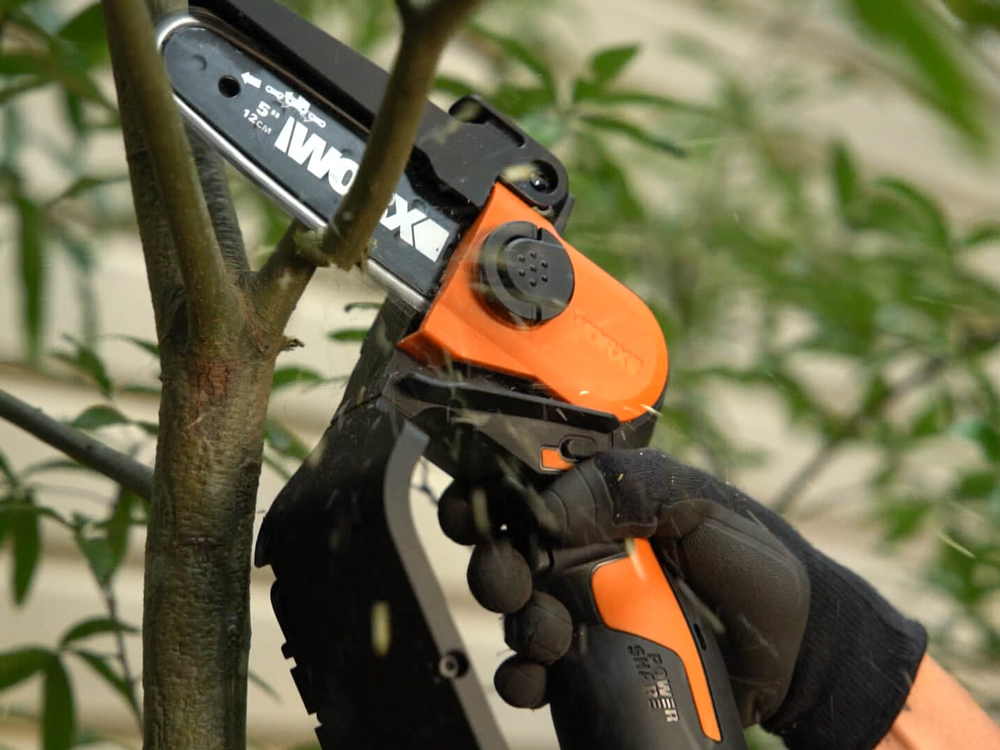


5.2 Configuration on fixed pole
Even with the pole configuration, they are the most challenging and uncomfortable pruners to use, again due to their size and weight. These aspects affect their convenience, requiring the operator more space and more effort to move with the machine during its use.
Shears, on the other hand, even when used on an extension pole, are able to cut in tighter spaces, and their light weight allows the operator to carry out longer and less tiring cutting sessions.
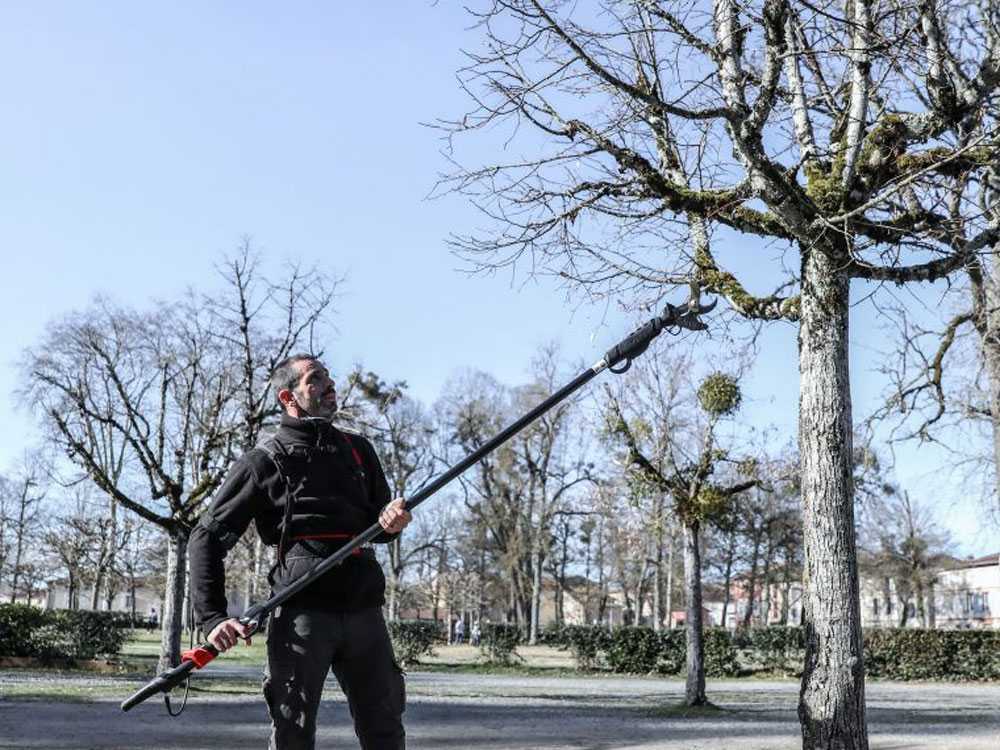
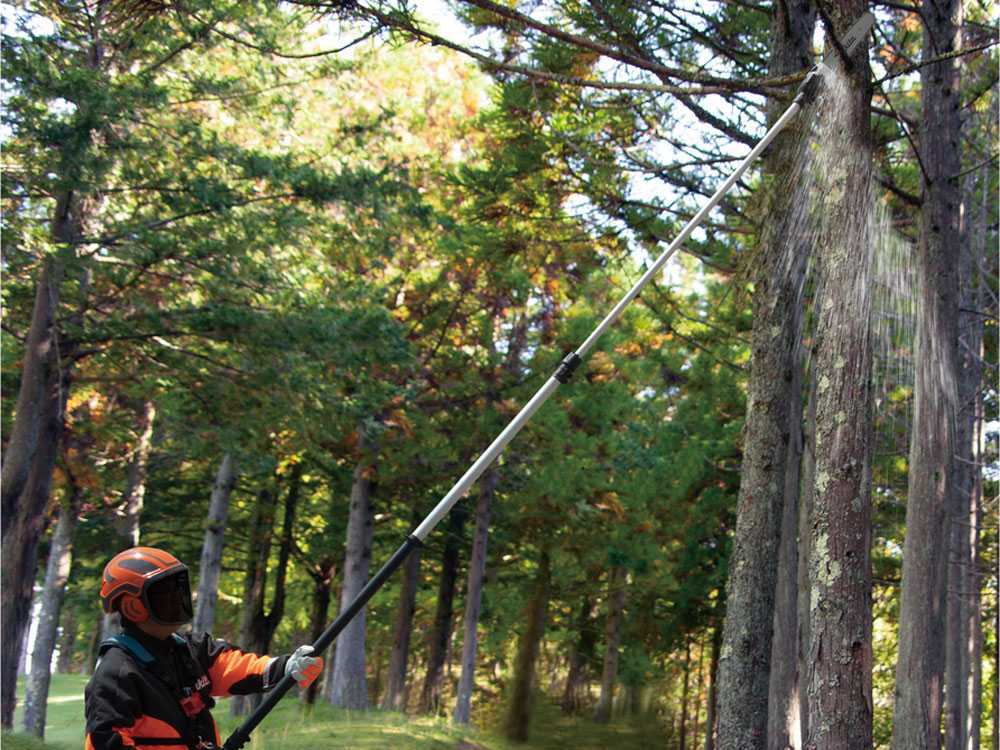


6. Weight and equipment
As previously stated, the size and weight can widely vary between pruners and pruning shears.
We have seen how pruners are larger and heavier than shears, an aspect that can significantly influence the choice between one and the other category. They can range from a minimum weight of 1.5 kg in the lightest models such as the electric (230V), battery and pneumatic models, up to 12 kg for petrol-powered backpack pruners.
Especially petrol-powered pruners, with or without a backpack, are the heaviest due to the presence of the engine, which alone constitutes a large part of the total weight.
The shears, on the other hand, can weigh from a minimum of 700 gr to a maximum of 4 kg when used on an extension pole.
| Manual configuration | Configuration on extension pole | Backpack configuration | |
| 2/4 stroke pruners |  | ||
| Electric Pruners (230V) |  |  | |
| Battery-powered pruners |  | ||
| Pneumatic pruners |  | ||
| Battery-powered electric shears | |||
| Pneumatic shears |  |
6.1 Backpack equipment
For petrol pruners and battery-powered electric pruners, it is also possible to configure them with the supplied backpack, which contains respectively the motor or the battery.


Even with this configuration, the main difference between the two categories is the total weight of the machine and its convenience.
In the backpack configurations of the battery-powered pruning shears, the weight, although greater than in the other configurations, remains low. With petrol pruners, on the other hand, there will be considerable weight due to the larger size of the engine and tool. So why choose this type of equipment since the weight increases?
For both versions, the backpack equipment is a more complex and heavier alternative, but essential for longer work sessions.
In fact, this type of configuration is recommended for operators who have to carry out long cutting sessions in large crops, where thanks to the backpack with padded backrest and various supports, back fatigue will be reduced as little as possible and, at the same time, arm fatigue will be reduced as the feed block is not directly fitted on the machine.