A comprehensive guide to purchasing a power generator to help you choose the best machine for your needs.
The Guide for Choosing the Best Power Generator
Complete and Curated by Real Experts in Electrical Engineering
Power Generators are part of a very complex universe within which it is not always easy to navigate, especially if one is a first-time user with little experience. This is because there are thousands of very different products on the market in terms of price, power and features, increasing the confusion of the user struggling with the purchase.
This guide was created with the aim of helping you choose the best power generator according to your needs and to better understand this type of product, explaining in a clear and simple way some fundamental aspects that most often are overlooked during the purchase phase.
CONTENTS
- 1. Introduction
- 2. 1500 rpm VS 3000 rpm
- 3. The 4 Most Common Mistakes Not to Make
- 4. The level of use
- 5. Power: KW e KVA
- 6. Country of manufacture, Materials and Brands
- 7. Single-phase or Three-phase
- 8. Quietness and noise
- 9. Power supply
- 10. Calculating the consumption of an electrical device
- 11. Places of use
- 12. Stabilized power generators: Inverters or AVRs
- 13. Start-up
- 14. Portable Power Station
1. Introduction
Power Generators (or Generating Sets) are devices capable of transforming mechanical energy into DC or AC current in order to power electrical appliances. These machines are essential if you need to have an autonomous source of electricity available in places without stable electrical sources, such as construction sites, isolated places, campgrounds, or where power distribution fails due to temporary outages or malfunctions (e.g., blackouts).

2. 1500 rpm VS 3000 rpm
A first major subdivision can be made by starting with the distinction between two macrocategories: 1500 rpm generators and 3000 rpm generators. The term “rpm” means “rotations per minute,” or the number of engine revolutions made in 60 seconds.
- The 1,500-rpm (rpm) generators are less commercial and are designed for heavier work, where it is necessary to operate for many consecutive hours or where industrial machinery needs to be powered (e.g., factories and construction sites);
- The 3000-rpm (rpm) generators are the most popular on the market and are recommended for purely emergency, occasional or short-term use.

1500-rpm power generator
of a hospital
1500-rpm power generator
of a factory
3. The 4 Most Common Mistakes Not to Make
- CONFUSING GENERATOR OUTPUT WITH ENERGY DEMAND
Most people think that in order to power a plant with a kilowatt total, it is enough to have a generator of the same energy output. Wrong. What not everyone knows is that most equipment needs more power to start up than it needs for normal operation, so-called “inrush energy.”
Example:
Imagine that you have to use an ordinary 3 HP compressor with a nominal consumption of 2.3 KW and power it with a power generator. The engine, however, will need 2-3 times its rated energy to start. Basically, we will need to rely on a generator of at least 7 KW with a 32A industrial outlet.
Remember: Buying an undersized generator can impair the life of the machine or make it totally inadequate for the required task, as well as dangerous in some situations.
| APPLIANCE | CONSUMPTION | INRUSH COEFFICIENT | CALCULATION | POWER NEEDED |
| Bulb | 100 watt | 1 | 100 x 1 | 100 watt |
| Electric stove | 1500 watt | 1 | 1500 x 1 | 1500 watt |
| Grinder | 280 watt | 1.5 | 280 x 1.5 | 420 watt |
| Circular saw | 800 watt | 3 | 800 x 3 | 2400 watt |
| Compressor | 1500 watt | 3 | 1500 x 3 | 4500 watt |
| Refrigerator | 250 watt | 3 | 250 x 3 | 750 watt |
| Air conditioner | 2000 watt | 3 | 2000 x 3 | 6000 watt |
- NOT KNOWING THE ACTUAL ABSORPTION OF THE MACHINERY TO BE POWERED
Certainly among the most important aspects is knowing the actual absorption of the system, machinery and device to be powered through our generator. Therefore, before you go ahead with the purchase, calculate well what the actual energy requirements of what you need to power are so that you have a generator that is up to the use you will have to put it to. - SINGLE-PHASE OR THREE-PHASE?
The third point concerns the type of power we need, which can be single-phase, that is, with a phase-to-neutral voltage of 230V, o three-phase (380-400V).
Wanting to simplify, we can say that to power a home or any civilian utility, we may need single-phase power, while if we need to power an industrial utility, we will need three-phase power.
Mistakenly, people think of buying a three-phase generator because they consider it “more powerful” and then use it in single-phase, resulting in 1/3 of the total generator capacity. This is because the power delivered by a three-phase generator must be spread over three phases, and each individual phase cannot deliver more than 1/3 of the total power. This is because the power delivered by a three-phase generator must be spread over three phases, and each individual phase cannot deliver more than 1/3 of the total power. In summary, a 9 kW genset can only deliver 3 kW per phase, no more and no less.
Be reminded that there are also generators on the market that can deliver the same power in both single-phase and three-phase and are marketed as “Full Power.”

16A schuko outlet (single-phase) 
16A industrial outlet (single phase) 
32A industrial outlet (single phase)

16A industrial outlet (three-phase) 
32A industrial outlet (three-phase) 
32A industrial outlet (three-phase)
- GIVE LITTLE IMPORTANCE TO END USE
Every product is designed and manufactured for a specific use, which may be industrial, professional, semi-professional, hobbyist or limited.
Very often we make the serious mistake of giving too much importance to the price of the product without considering its actual suitability, ending up buying a machine that is not up to the use one has to make of it. Basically, this happens both because of an excess of superficiality at the time of purchase and because many stores (physical and online) do not adequately clarify this very important aspect or not at all. To avoid making such a mistake, remember to gather sufficient technical information before purchase to get a good understanding of whether the product meets your real needs.
4. The level of use
As we have said repeatedly, it is essential to choose a power generator in relation to the use it will be put to.
There are 5 levels of use, namely:
- LIMITED: The generator can be used for occasional and not prolonged work sessions.
- HOBBYIST: The generator can be used for work sessions that are not too frequent and not too prolonged (maximum 4 consecutive hours). In this category, we already find power generators of good workmanship and quality, equipped with a 4-stroke gasoline engine, whose size is between 1 and 7 kW in power.
- SEMIPROFESSIONAL: It concerns those models that come very close to the professional level, especially in terms of performance and power (most of these machines are between 4 and 7 kW in power). Although superior to those for hobby use, these gensets are not suitable for prolonged, intensive and too frequent use. Again, it is recommended not to exceed 4 hours of continuous use.
- PROFESSIONAL: Included in this category of use are all those machines that, in addition to their power output, are made with technologies and materials suitable for heavy and intensive use. A professional power generator is an instrument of high quality and reliability.
- INDUSTRIAL: In this case we are talking about of high quality equipment and of great performance, designed to work intensively and for long periods of time, as in the case of industries, construction sites, companies and others. Generally, 1500-rpm generators fall into this class.

When in doubt, we advise you to always opt for the highest category. It is true that you will most likely go and spend a little more, but with the certainty of getting your hands on a product of higher quality and reliability, which will hardly lead us to say that we made a wrong purchase.
5. Power: KW e KVA
Power generators of various power ratings can be found on the market, from the smallest under 3 KW to those over 20KW, specifically for industrial-level use. The Power can also be calculated and given in KVA (KiloVolt-Ampere) , and to get the power in KW (Kilowatts) simply multiply the value in KVA by the power factor, which is usually 0.8. For example, a 5 KVA generator will correspond to 4 KW (5 x 0.8 = 4).
Power in Kilowatt = Power in KVA x Power Factor (0.8)
6. Country of manufacture, Materials and Brands
- COUNTRY OF MANUFACTURE
As is the case with so many other products, the country of manufacture of a power generator is in itself an indicator of quality; an important aspect that is very often given little consideration or even overlooked. Think of a Chinese product, for example, that is inferior in quality of internal components, assembly, and materials to an Italian or German product. - MATERIALS
When choosing a generator, we cannot fail to consider the quality of the materials with which it is manufactured, especially if we know that it will be used in open environments. Machinery made of good materials that are unlikely to rust is definitely synonymous with quality, safety and performance. - BRANDS
It may seem obvious, but it is always worth repeating: a brand name is not always synonymous with reliability, but it is also true that a machine produced by a company with years of experience in the field will almost certainly be “one step ahead”. The reason is simple: a brand that has been operating for years in a given sector can boast such a high degree of experience and knowledge of consumer needs that it can build quality equipment in line with the standards demanded by the market. In addition to this, an “established” brand is also reliable in terms of local service and spare parts.
Some of the best brands include: Pramac, Honda, TecnoGen and Mosa

Hyundai DHY8500SE-T 
Energy EY-12TB
Briggs&Stratton Vanguard Engine
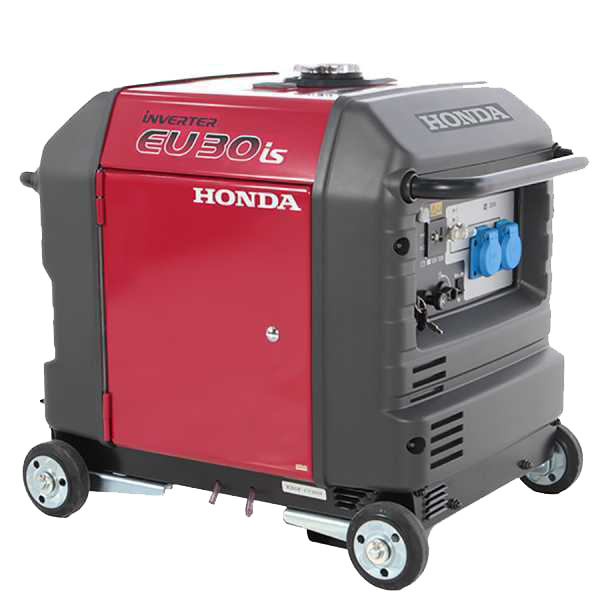
Honda EU30is
Honda GX200 Engine
7. Single-phase or Three-phase
Among the elements to take into consideration when choosing a genset is the voltage, which, as we explained in the previous paragraphs, can be: single-phase or three-phase; the former (single-phase) are mostly used in the domestic sphere, while three-phase have a more professional-industrial purpose, delivering up to 380-400 Volts and are used precisely in situations where it is required to power high-draw machinery.

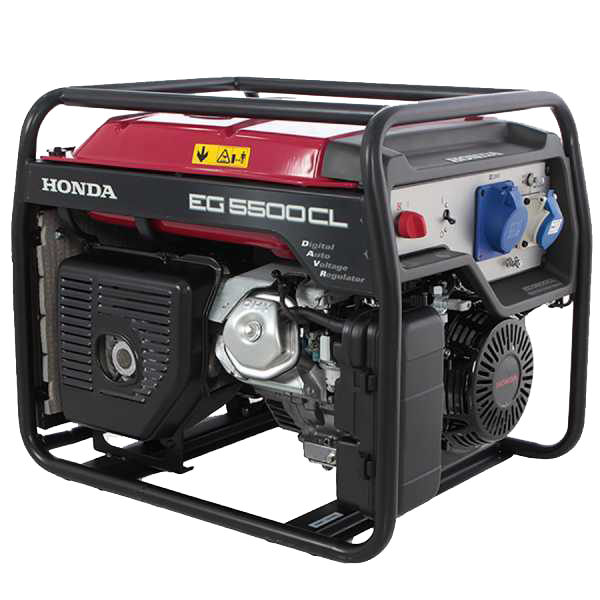
Single-phase power generator
Honda EG 5500CL
Three-phase power generator
Honda ECT 7000
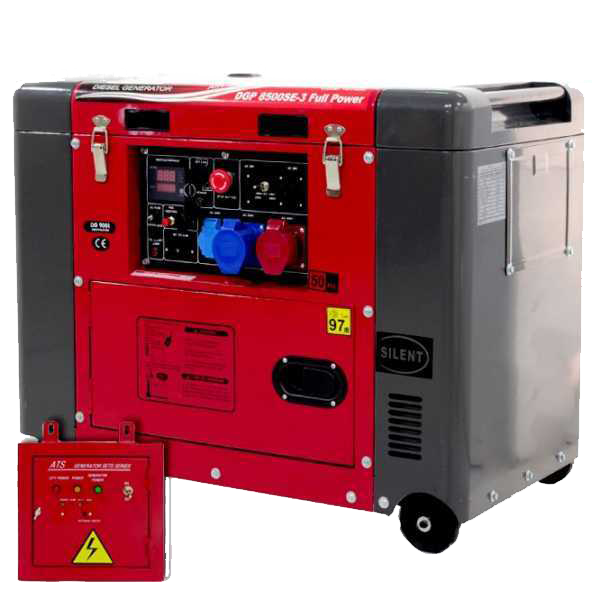
Full-power power generator
GeoTech Pro DGP8500SE-3
As we explained above, while a single-phase cannot be used as a three-phase, on the other hand a three-phase can do the work of a normal single-phase generator, but implying a reduction to one-third of its working power.
Example: A 6 KW three-phase generator can also work in single-phase but at 2 KW power and not 6 KW as you may mistakenly think.
8. Quietness and noise
A very important aspect for a genset is the degree of noise, especially if it is intended to be used in some particular environments, such as homes, apartment buildings, or in all those settings where there are very strict rules on noise pollution. In all these cases there is only one solution: rely on a soundproof (or silenced) power generator . We refer to gensets with silent engines and high-performance soundproofing guards that wrap around it to attenuate noise, leaving openings at the exhaust and alternator.

TecnoGen H8000SS Silenced petrol power generator 
BlackStone B-iG 4000 Petrol inverter power generator
Unlike non-silenced models, which are suitable for shorter uses, silenced (or supersilenced) gensets are recommended for domestic use and for all situations where prolonged use is required.
Indicatively, a 2-3 KW generator operates at 70 decibels, the same degree of noise as a loud conversation.
To avoid unpleasant inconveniences, we recommend that you always know the decibels produced by your running generator and check the current municipal regulations on sound emissions and noise pollution, which, remember, may vary from territory to territory.
9. Power supply
Many start making an initial selection right from the type of fuel required.
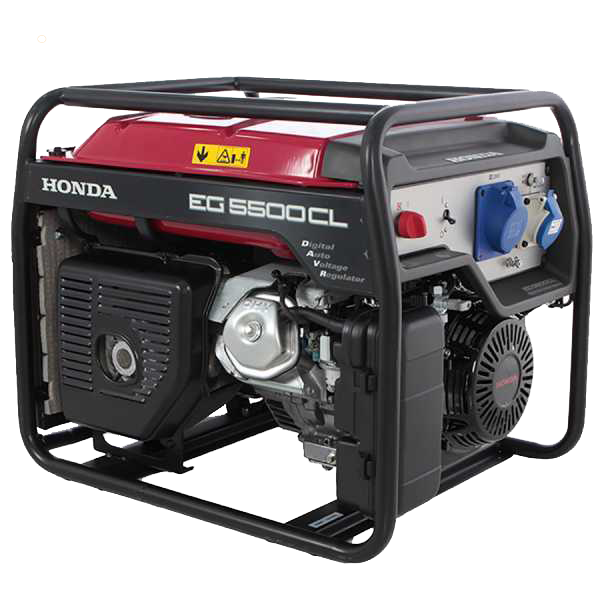

9.1 Petrol power generators
- PETROL
Petrol power generators are cheaper and slightly quieter than the other types, plus they have the great advantage of having a compact shape and a lower weight, which makes them easier to move around.
They are generally less powerful than diesel gensets and are recommended for short and occasional use.
A major strength of petrol powered models is its drive, which compared with diesel ones have a convenient pull start.
Petrol power generators are cheaper and slightly quieter than the other types, plus they have the great advantage of having a compact shape and a lower weight, which makes them easier to move around.
They are generally less powerful than diesel gensets and are recommended for short and occasional use.
A major strength of petrol powered models is its drive, which compared with diesel ones have a convenient pull start.

9.2 Diesel power generators
- DIESEL
Diesel generators are undoubtedly the most popular on the market and the most widely used for intensive uses. In addition to reducing fuel consumption and consequently fuel expenses, diesel is more environmentally friendly and safer, since it is less flammable than petrol. The main disadvantages of diesel generators are precisely their noise (Compared to a petrol generator, these generators are less silent and therefore more limited under this aspect) and the weight greater.
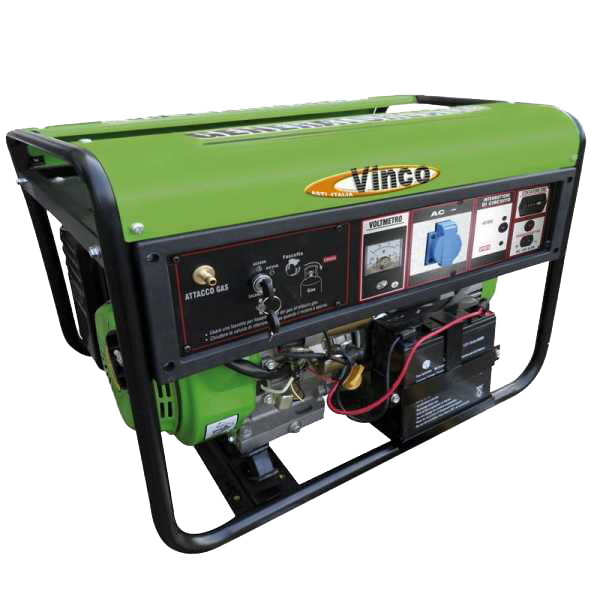

9.3 LPG or methane power generators
- LPG or METHANE
In recent years, LPG or Methane power generators have become very popular, a type that is more environmentally friendly and economical.
Unlike the more common petrol or diesel-powered generators, all those powered by natural gas, such as precisely LPG or methane, are able to work without producing strong odors, typical of the models mentioned above.
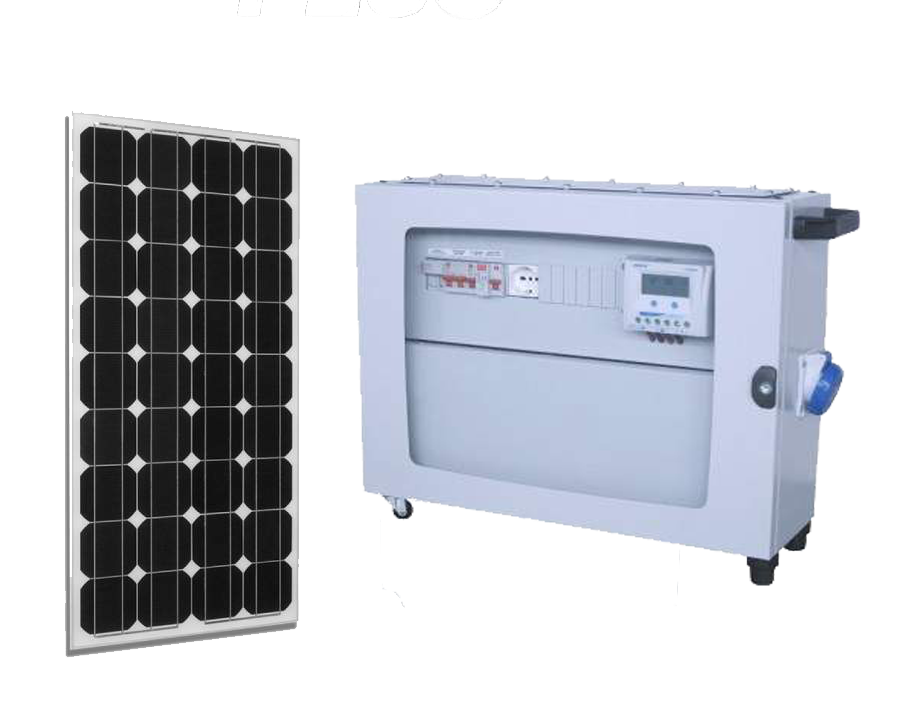

9.4 Photovoltaic generator sets
- SOLAR POWER
To conclude, if we are “green” and very environmentally conscious people, we can consider solar-powered generators. Photovoltaic power generators can be connected to regular solar panels to get 100 percent clean and significantly more cost-effective energy.
10. Calculating the consumption of an electrical device
To be sure of the real starting power of our machinery, we have four possible solutions:
- Rely on a current consumption meter (current clamp);
- Contact the manufacturer directly and ask for the value of peak absorption, also known as “inrush.” In this case, it should be specified that the device will be powered by a generator;
- Consult your local electrician.
In order to calculate the power required to supply the appliances in our possession, we will have to perform a simple calculation, which will identify two values for each electronic device to be used: Consumption and Inrush coefficient. These two values should then be multiplied by each other to obtain the power needed for each tool.
Power = Rated consumption x Inrush coefficient
(as shown in the chart above)
11. Places of use
Before proceeding with the purchase of a genset, there is another key aspect to keep in mind, which is where the machinery will be used: Where will it be placed? Will it have to be moved between work sessions or will it remain fixed in one place? What power supply does it have? Is it silenced?
For example, if we have a stationary generator, then we will have to place it in a cool, dry and well-ventilated environment. As we have already mentioned, power generators emit exhaust fumes, and that is precisely why it is recommended to place them in open places, also applying covers to protect it from any weather that may occur during power supply. On the other hand, if we decide to use it indoors, we must take care to locate a sufficiently ventilated spot, both to let the generator “vent” without incurring accidents due to the gases given off and to prevent it from overheating.
Equally important is the connection to the ground drain, as required by safety regulations in order to avoid danger to people and the machinery itself. This procedure is to be carried out by grounding a pole with associated resistive calculation, and it is normally done by an electrician.
The last aspect to consider is noise. As mentioned above, a genset that is particularly noisy or otherwise produces such noise that it disturbs neighbors (homes, businesses, hospitals, schools, offices, and so on) or exceeds the decibels allowed by law (e.g., municipal regulations) cannot be used. In these cases, the only solution is to rely on silent or low-noise models that can absorb or attenuate the vibrations and noise emissions produced by the operation of the machinery.
As for power generators for domestic use, we recommend those with a noise level between 55 dB and 70 dB, so that it can be kept in operation even at night without causing a disturbance.
Below is a small summary chart of the general characteristics that each model should have based on the environment in which it is to operate:
| ENVIRONMENT | POWER SUPPLY | TECHNOLOGY | STARTER TYPE | GENERAL FEATURES | |
 | Petrol | Inverter | Pull-starter | Due to space issues, the generator will have to be compact, easily transportable, light in weight, and with good power. | |
 | Petrol | Inverter | Pull-starter | They are easily transportable groups with low weight and limited power (usually powering booth lights). | |
 | Petrol Diesel | Unstabilized generator | Pull-starter |
| |
 | Fuel-mix Petrol Diesel | AVR | Electric or Pull-starter | DIY equipment is not particularly complex and can be powered by generators with the AVR system. | |
 | Petrol Diesel | AVR + ATS | Automatic Electric | Generators connected to safety equipment are usually generators with automatic start-up panel. | |
 | Petrol | AVR + ATS | Automatic Electric | They are generators, both petrol and diesel, equipped with an ATS panel (diesels allow less fuel depletion over time), which allows automatic startup in case of power failure. |
12. Stabilized power generators: Inverters or AVRs
In addition to the place of use, it is important to be clear about what equipment will be connected to our generator. For example, if the genset is to power a home, RV, or boat, we already know that it will have quite a few sensitive loads, such as TVs, household appliances, and devices quite susceptible to dangerous voltage surges capable of compromising or severely damaging them.

Power generator to power a booth 
Wheeled generator
for DIY
Power generator
for RVs
Household power generator
The main systems found in stabilized generators are: inverter or AVR.
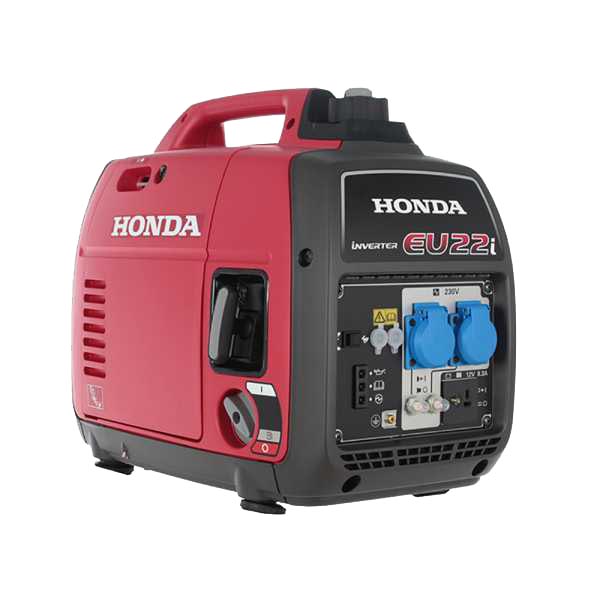
12.1 Inverter power generators
- INVERTER POWER GENERATORS
This type of generator represents the most suitable choice for having stable, constant, clean energy, but above all without voltage fluctuations. The emitted electric current has a purer ( and therefore perfectly stabilized) sinusoidal waveform, making it suitable for use with more sophisticated domestic or professional equipment with an electronic board (power tools, computers, TVs, home appliances, etc.), in RVs, boats, booths, or at fairs and events.

Honda EU70is Inverter Power Generator 
Honda EU22i Inverter Power Generator
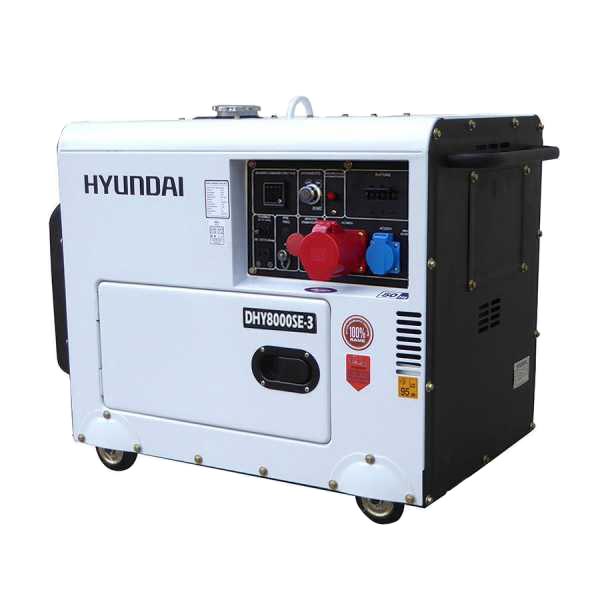
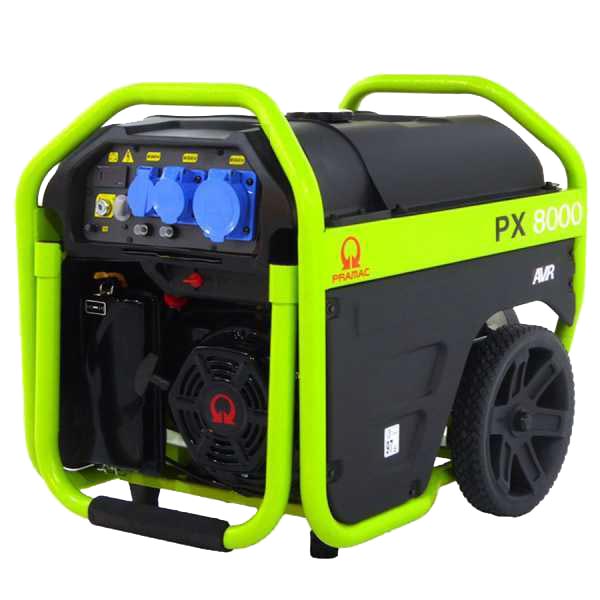
12.2 Power generators with AVR
- POWER GENERATORS WITH AVR SYSTEM
The AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator) system, also known as “Voltage Regulator“, is recommended for the most common uses and is intended to keep the operation of the machine constant and in the most efficient regime. This system not only ensures the smooth operation of the machine but also ensures the durability of the connected equipment.
In addition, AVR allows the output voltage to be kept constant, ensuring fewer current dips or spikes.

Power generator with AVR
Energy EY-16TBE
Power generator with AVR
Hyundai DHY8000SE3
Power generator with AVR
Pramac PX 8000
13. Start-up
Gensets can have various types of start-up: Pull-starter or electric/automatic start.
- PULL-STARTER
The mechanism of the pull-starter or starter rope consists of a rope wound on a pulley and held by a spring. To start the engine, you need to pull the rope with the right force to give an initial push that will start the engine.
- ELECTRIC START
In this case there is an electric start engine which runs for a few seconds until the engine begins to run normally.

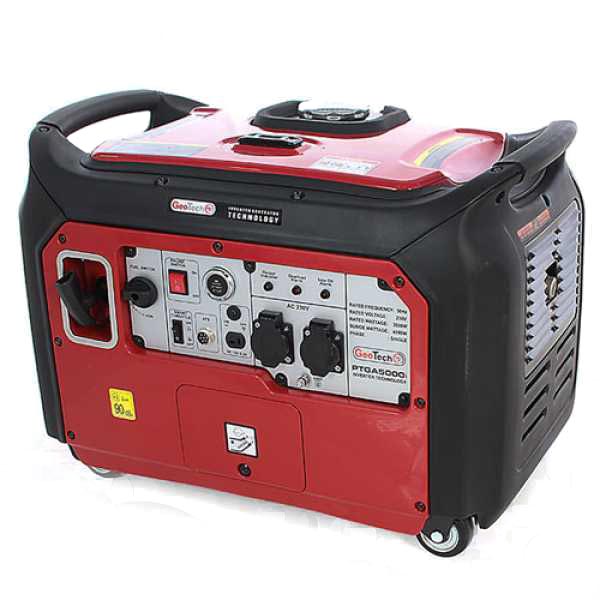
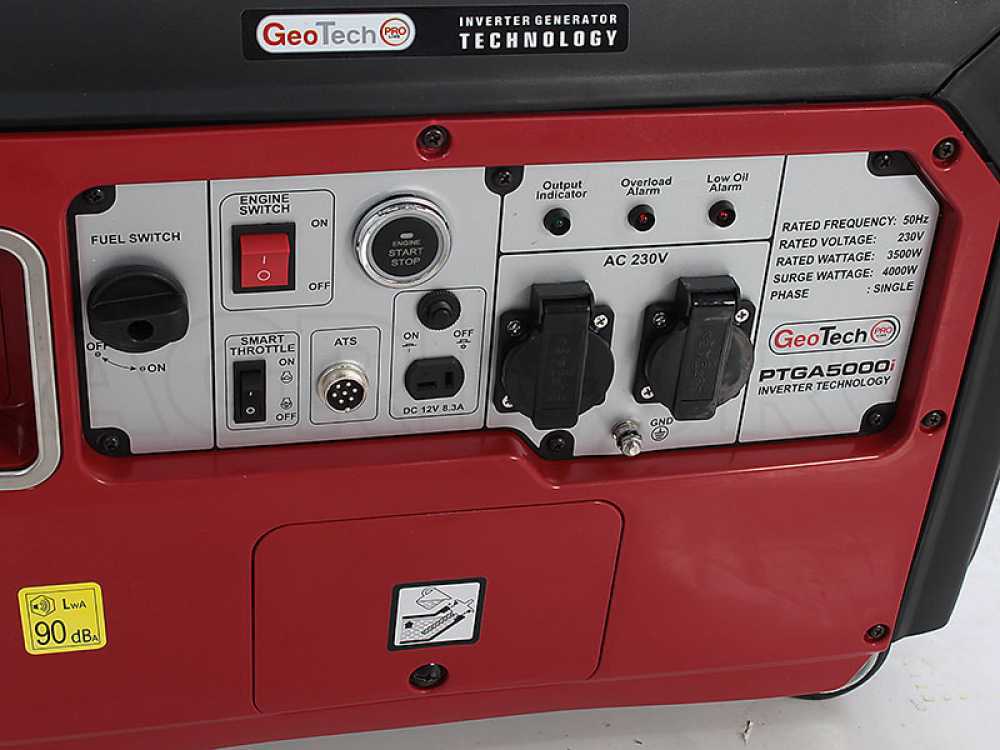
GeoTech PTGA5000 Power Generator 
Electric start panel with “Start/Stop” button
- AUTOMATIC START (ATS)
Some generators may have an automatic start (integrated in some models and external in others), which is usually referred to as ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch).
This system allows the power generator to start up completely autonomously in case of power failure without any human intervention. In fact, thanks to the ATS system, we are able to interface our device with the public grid, enabling it to start up even when the power supply is absent. This is precisely why they are widely used in homes at risk of power disconnection, in security companies, in basements at risk of flooding, for cold storage or potential emergency situations.

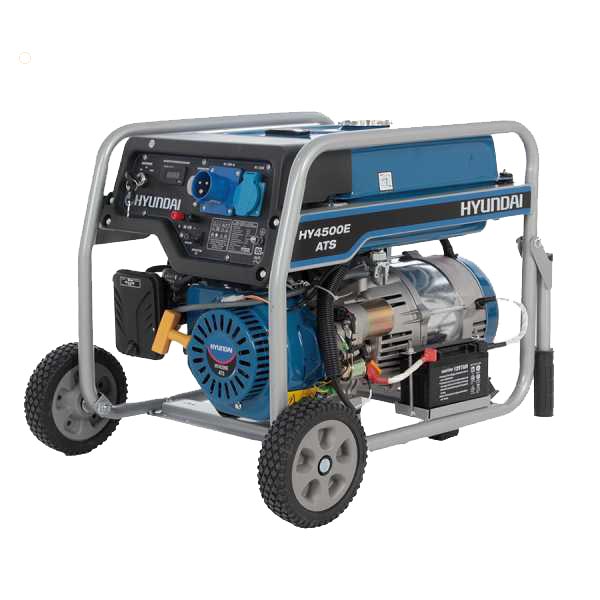
Hyundai HY4500E Power generator with integrated ATS
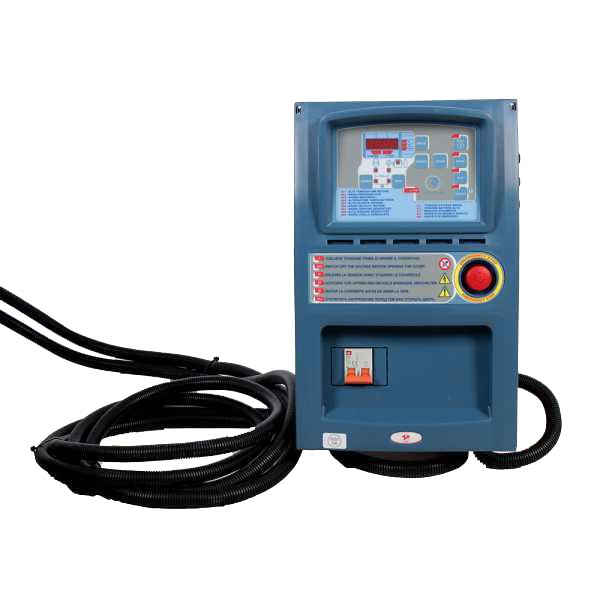
External ATS system 
Energy EY-7TBE-A Power generator with external ATS system
14. Portable Power Station
In this our guide to generator sets and power generators, we could not fail to also mention the portable power stations. The latter are not true power generators as they are more like rechargeable batteries. This is why they are also called portable power stations or portable power accumulators.
However, both power generators and portable power stations are two systems for obtaining electricity in the absence of the power grid.
In particular, portable power stations, are devices that offer a versatile and reliable solution for various energy needs in any location, whatever it may be by allowing you to have a portable power reserve thanks to built-in batteries. Therefore, they are ideal for powering a wide range of devices, from smartphones and laptops to power tools and small appliances.
What is a power station for then?
Portable power stations are perfect for:
- Powering or charging electronic devices: smartphones, tablets, laptops, cameras, drones.
- Powering small single-phase household appliances: fans, mini refrigerators, lamps, portable TVs.
- Operating power tools: drills, hacksaws, screwdrivers, compressors.
- Providing electricity in emergency situations: power outages, power failures, camping
14.1 What are the differences between portable power stations and power generators?
As much as portable power stations and generator sets are two systems for obtaining electricity in the absence of the power grid, they have substantial characteristics and differences. We have listed the main ones in the chart below:
| PORTABLE POWER STATION | GENERATOR SETS | |
| POWER SUPPLY | Rechargeable lithium batteries. | Gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. |
| NOISE AND EMISSIONS | Silent, no gas emissions. | Noisy, with gas emissions. |
| POWER | Variable, from a few hundred watts to several kilowatts. | High, from several kilowatts to tens of kilowatts. |
| AUTONOMIA | Limited, need periodic recharging. | Wide, extended operating range. |
| PORTABILITY | Elevated due to small size and weight. | Also suitable for powering power tools and machinery. |
| USES | Ideal for electronic devices, small appliances, lighting. | Also suitable for powering power tools and machinery. |
14.2 How many types of portable power stations are there? What are the main differences?
Portable power stations, are mainly divided into two types: wheeled and non-wheeled. Below we have listed the main differences between the two types while also explaining when it is most appropriate to use them.
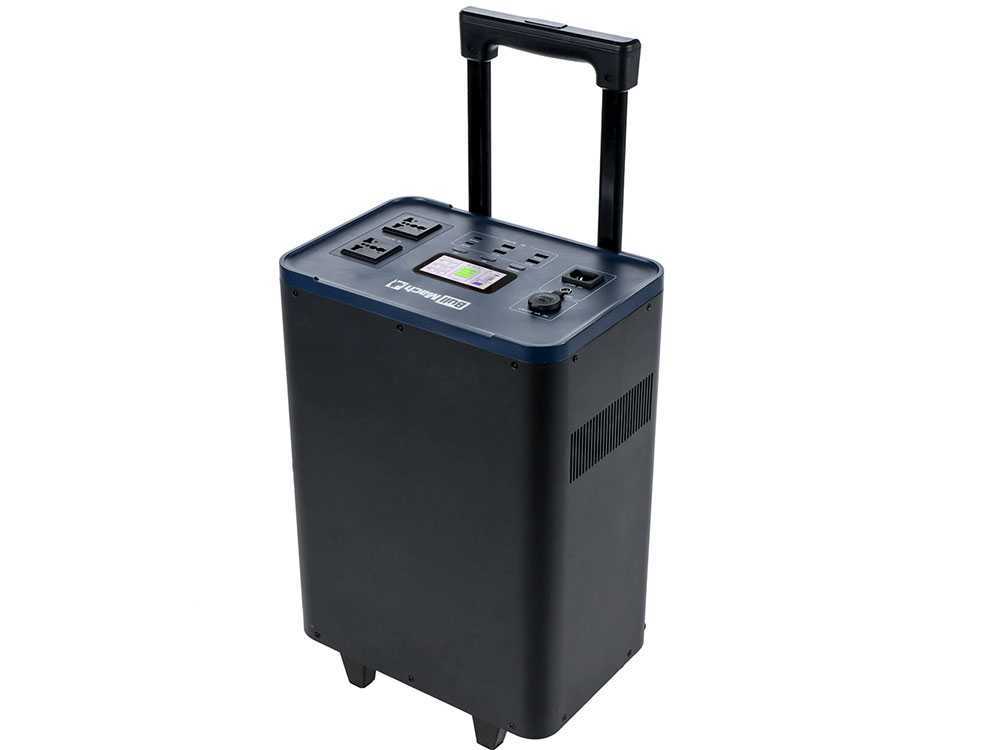
Wheeled power stations:
- Features: They are called wheeled because they are equipped with wheels and a handle that are used to make them easier to transport since they are larger in size and weight than non-trolley versions. Wheeled models usually have higher Amperage, so they also have more batteries, or at least larger batteries, inside them. It is precisely this that affects their weight and size, increasing them significantly. Some models, for example, weigh as much as 35 kg distributed in about 50x25x30 cm. In addition, wheeled portable energy accumulators also have a higher capacity of power output. For all these reasons, they also generally have a higher price than non-wheeled models.
- Uses: Wheeled power stations are ideal for on-the-go use and for powering devices with high power consumption. They offer greater operating range . They are distinguished by being strong and durable.

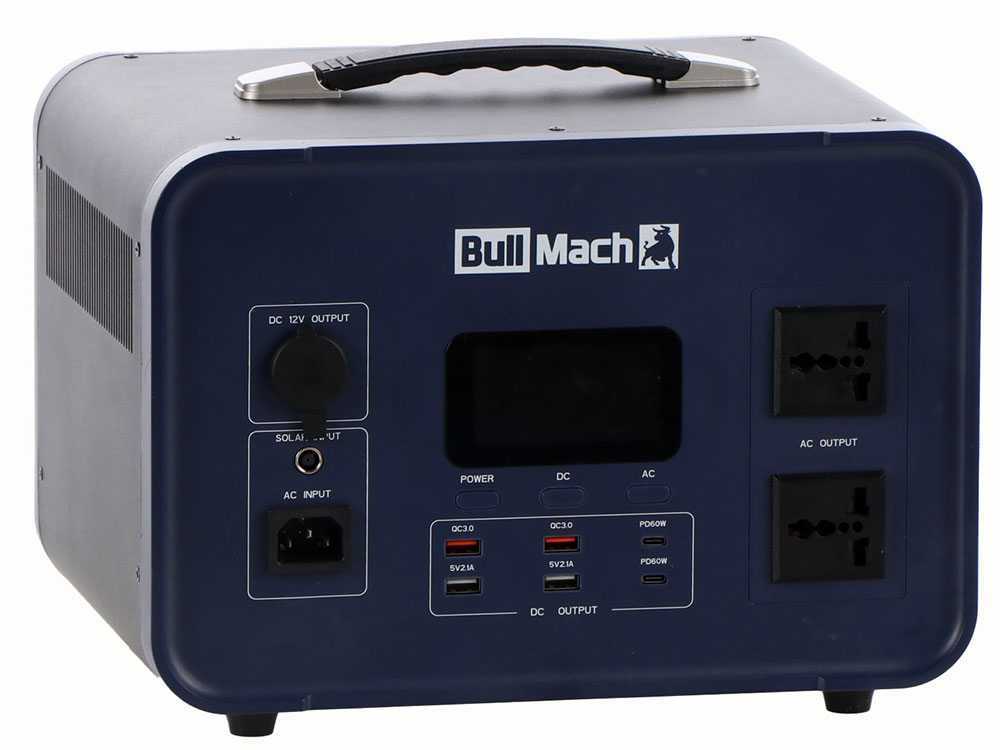
Portable power stations:
- Features: Compared with wheeled models, they have reduced size and weight. For example, the weight of these portable power stations is around 19 kg in the most powerful models with dimensions around 32x28x24 cm. This makes them relatively easy to transport and store compared to a wheeled power stations. As we saw earlier, smaller size means smaller battery capacity and power output, characteristics that affect their use. As a result, the price of portable power stations is generally lower than the wheeled power stations .
- Uses: Practical and versatile for everyday use. Suitable for powering electronic devices and small household appliances. Silent and light.

14.3 Technical characteristics of power stations
Regardless of whether the portable power station is wheeled or not, the main technical features that these portable power stations share are as follows.
Power:
The range of portable power stations offers different power options, from 500 watts to 3000 watts, to meet the needs of every user. 1000-watt models are ideal for electronic devices and small appliances, while 2000-watt and 3000-watt models can also power power tools and machinery.
Recharge:
Portable power stations offer different charging modes:
- Standard charging: via household power outlet.
- Solar charging up to 60V/300W: with compatible solar panel (sold separately).
- Fast AC charging: for quick charging from high-voltage power outlets.
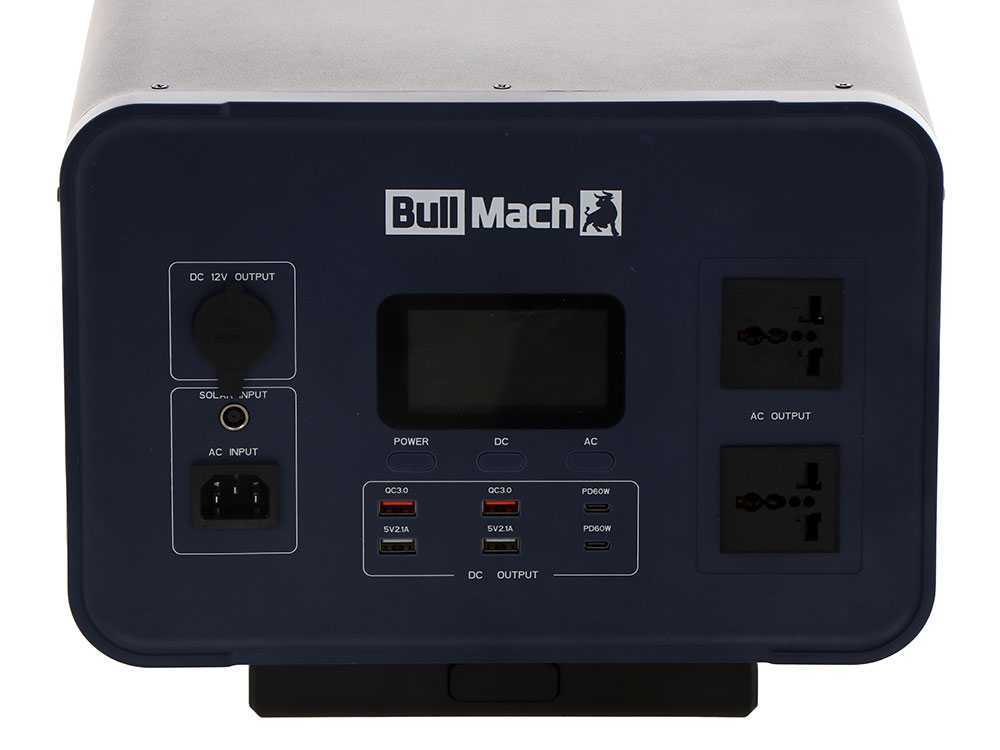
Ports and Outputs:
Portable power accumulators have different ports and outputs to power different devices. They are usually equipped with:
- One or more continuous power ports: to power devices with constant consumption.
- Peak power port: for powering devices with high peak consumption.
- DC ports: 12V, 10A, and a cigarette lighter port
- One or more standard USB-A and USB-A QC3.0 ports for charging smartphones, tablets and other USB devices.
- Type-C ports offering PD 60W and PD 100W.

Safety and security:
Portable power stations are equipped with various protections to ensure safe operation:
- Protection against short circuit.
- Overload protection.
- Protection against overheating.
- Overvoltage protection.
Important: Grounding
Portable Power Stations are grounded and certified to all electrical safety standards and all CE standards..
Lifespan:
Portable power station batteries have a lifespan of more than 500 cycles up to 80 percent capacity, ensuring long-term use.
14.4 Uses
Portable power stations are distinguished by their practicality and compactness, making them perfect for a variety of situations:
- Camping and outdoor activities: enjoy nature without sacrificing the comforts of home by charging your electronic devices or powering lighting and small appliances.
- Emergencies and blackouts: in the event of power outages, portable power stations provide emergency power for essential devices.
- Work on the go: offer a reliable energy source for operating power tools and laptops on construction sites or any location with no sockets.
Of course, the choice of the type of portable power station depends on your specific usage needs. Therefore, before purchasing one, it is wise to think carefully about their use by also consulting the technical characteristics of the appliances you want to power.